 The men from Detroit will jet into Washington tomorrow -- presumably going commercial this time -- to make another pitch for a taxpayer rescue. Meanwhile, in the other American auto industry you rarely read about, car makers are gaining market share and adjusting amid the sales slump, without seeking a cent from the government.
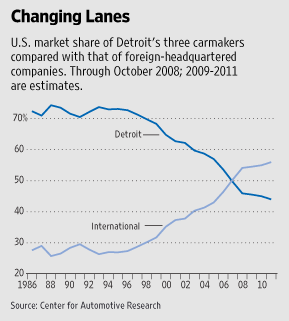
The men from Detroit will jet into Washington tomorrow -- presumably going commercial this time -- to make another pitch for a taxpayer rescue. Meanwhile, in the other American auto industry you rarely read about, car makers are gaining market share and adjusting amid the sales slump, without seeking a cent from the government.These are the 12 "foreign," or so-called transplant, producers making cars across America's South and Midwest. Toyota, BMW, Kia and others now make 54% of the cars Americans buy (see chart above). The internationals also employ some 113,000 Americans, compared with 239,000 at U.S.-owned carmakers, and several times that number indirectly.
The international car makers aren't cheering for Detroit's collapse. Their own production would be hit if such large suppliers as the automotive interior maker Lear were to go down with a GM or Chrysler. They fear, as well, a protectionist backlash. But by the same token, a government lifeline for Detroit punishes these other companies and their American employees for making better business decisions.
The root of this other industry's success is no secret. In fact, Detroit has already adopted some of its efficiency and employment strategies, though not yet enough. To put it concisely, the transplants operate under conditions imposed by the free market. Detroit lives on Fantasy Island.
Consider labor costs. Take-home wages at the U.S. car makers average $28.42 an hour, according to the Center for Automotive Research. That's on par with $26 at Toyota, $24 at Honda and $21 at Hyundai. But include benefits, and the picture changes. Hourly labor costs are $44.20 on average for the non-Detroit producers, in line with most manufacturing jobs, but are $73.21 for Detroit (see chart below).
 This $29 cost gap reflects the way Big Three management and unions have conspired to make themselves uncompetitive -- increasingly so as their market share has collapsed (see the top chart above). Over the decades the United Auto Workers won pension and health-care benefits far more generous than in almost any other American industry. As a result, for every UAW member working at a U.S. car maker today, three retirees collect benefits; at GM, the ratio is 4.6 to one (see chart below).
This $29 cost gap reflects the way Big Three management and unions have conspired to make themselves uncompetitive -- increasingly so as their market share has collapsed (see the top chart above). Over the decades the United Auto Workers won pension and health-care benefits far more generous than in almost any other American industry. As a result, for every UAW member working at a U.S. car maker today, three retirees collect benefits; at GM, the ratio is 4.6 to one (see chart below). The international producers' relatively recent arrival has spared them these legacy burdens. But they also made sure not to get saddled with them in the first place. One way was to locate in investment-friendly states. The South proved especially attractive, offering tax breaks and a low-cost, nonunion labor pool. Mississippi, Alabama, Tennessee and South Carolina -- which accounted for a quarter of U.S. car production last year -- are "right-to-work" states where employees can't be forced to join a union.
The international producers' relatively recent arrival has spared them these legacy burdens. But they also made sure not to get saddled with them in the first place. One way was to locate in investment-friendly states. The South proved especially attractive, offering tax breaks and a low-cost, nonunion labor pool. Mississippi, Alabama, Tennessee and South Carolina -- which accounted for a quarter of U.S. car production last year -- are "right-to-work" states where employees can't be forced to join a union.
~Today' WSJ editorial America's Other Auto Industry






No comments:
Post a Comment